What is Parallel Tracking?
Parallel Tracking is a method designed to enhance user experience by minimizing page load delays caused by redirect links. Instead of processing redirects sequentially, Parallel Tracking allows tracking and redirections to occur in the background, while users are sent directly to their intended destination. This approach aims to reduce bounce rates and increase conversion rates by ensuring a smoother and faster user journey.
For standard tracking, when a user clicks on an affiliate link, they are redirected through a tracking server before reaching the final destination. Even though this redirection often takes only milliseconds, slow networks or mobile connections can introduce noticeable delays. Parallel Tracking mitigates this by handling tracking separately in an asynchronous process, improving site load speed.
The Importance of Speed in Web Performance
Speed has always been a key factor in web development, influencing user behavior and engagement. Studies by Pingdom show that:
-
Pages that load within 2 seconds experience an average bounce rate of 9%.
-
A page load time of 3 seconds increases the bounce rate to 38%.
-
As load times exceed 5 seconds, the bounce rate skyrockets.
Google developed Parallel Tracking to improve the speed of ad-driven traffic, ensuring that tracking does not interfere with user experience. According to Google:
"Parallel tracking helps load your landing page more quickly which can reduce lost visits. That can lead to increased conversions and improved ad performance. Parallel tracking sends customers directly from your ad to your final URL while click measurement happens in the background (without sending them to the tracking URLs first)."
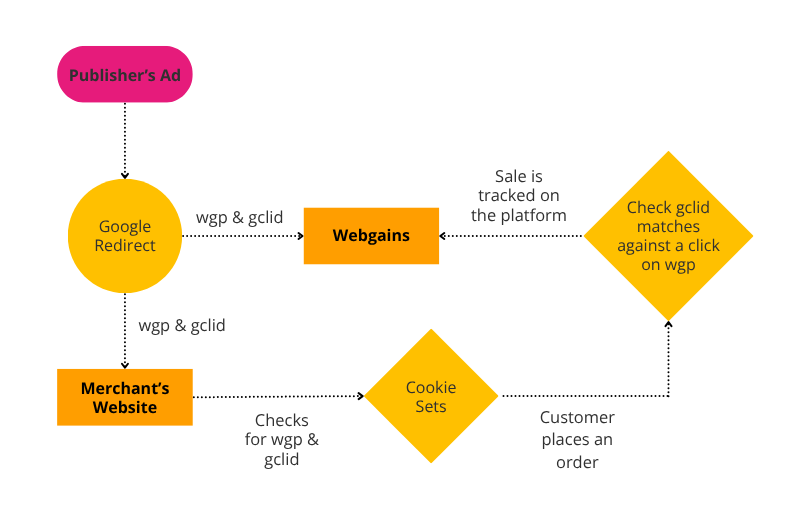
How Webgains Supports Google’s Parallel Tracking
Webgains fully supports Google's approach to parallel tracking. Publishers can configure Google Ads settings to specify which GET parameters are preserved in the final URL. Webgains utilizes this feature to track whether a merchant was promoted by one of our publishers.
Key Tracking Parameters:
-
gclid – A unique identifier generated by Google for tracking individual ad clicks.
-
wgp – A static value representing Webgains program IDs.
When a user lands on a merchant's site, the Webgains landing page script scans for these parameters. If both are present:
-
The gclid value is treated as wgu (Webgains unique click identifier).
-
Using wgp, Webgains can record the first-party cookie and fingerprint when the landing page script is fired.
How Parallel Tracking Works with Webgains
Step 1: Click Tracking
When a user clicks a Google ad, Parallel Tracking sends them directly to the merchant's landing page while tracking occurs in the background. Google identifies Parallel Tracking clicks by appending gb=1 to the request.
Step 2: Landing Page Processing
Once on the merchant’s landing page:
-
The Webgains script extracts gclid and wgp from the URL.
-
If both values exist, Webgains creates a first-party cookie for tracking purposes.
Step 3: Conversion Tracking
At checkout:
-
The front-end script retrieves the stored gclid from the cookie.
-
The transaction details are updated with gclid, allowing Webgains to attribute the sale to the correct publisher.