Explanation of Attribution
Attribution refers to the process of identifying which marketing touchpoints or interactions a customer experiences before making a conversion or purchase. It determines how credit for a sale or action is assigned to different marketing channels and activities. Effective attribution models help businesses understand which strategies contribute most to conversions, enabling more informed decision-making.
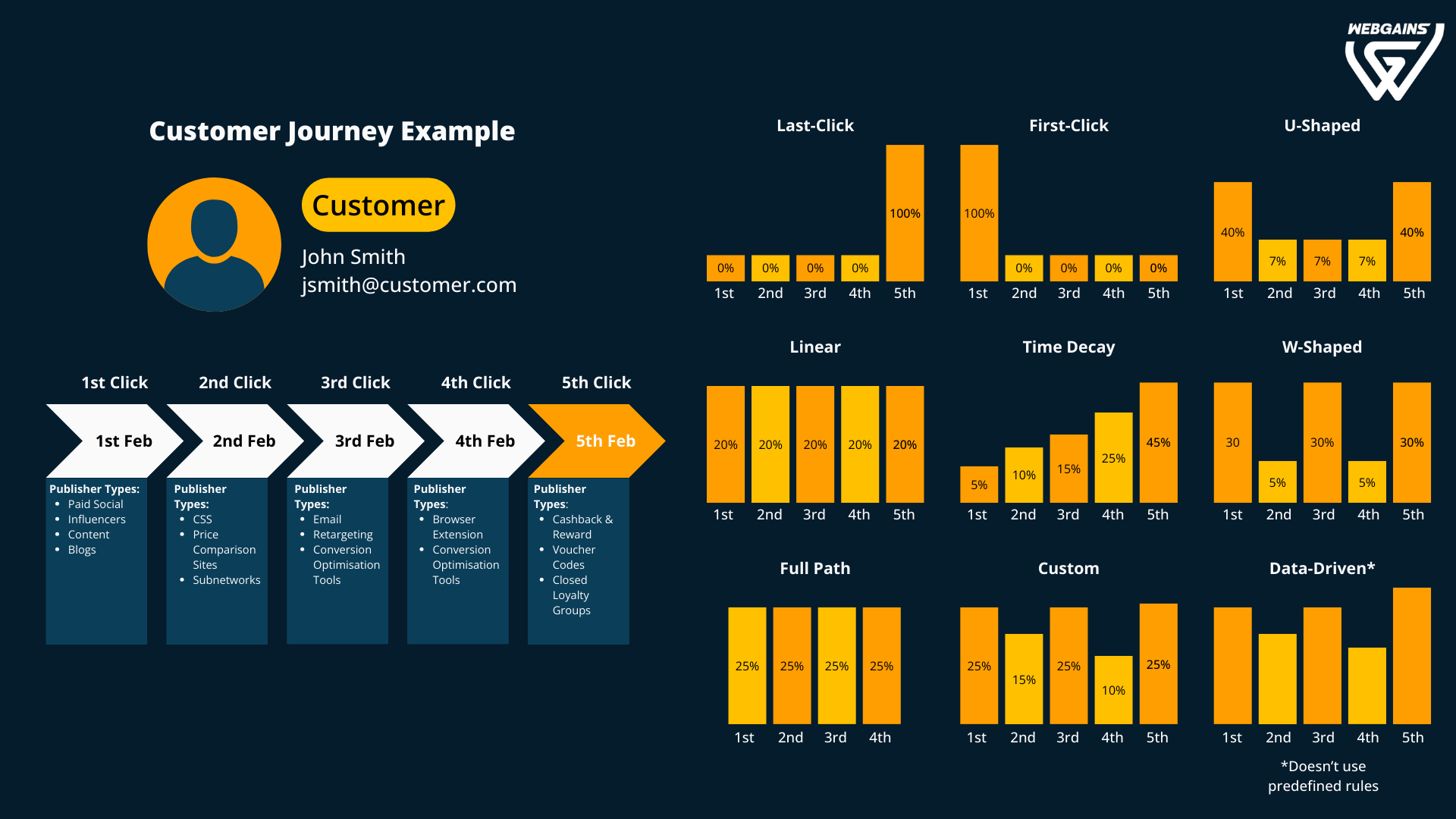
Common Attribution Models
-
First-touch Attribution: Assigns all credit to the first interaction.
-
Last-touch Attribution: Assigns all credit to the last interaction before the conversion.
-
Linear Attribution: Distributes credit evenly across all touchpoints.
-
Time-decay Attribution: Gives more credit to interactions closer to the conversion event.
-
Data-driven Attribution (GA4): Uses machine learning to distribute credit across multiple touchpoints based on their likelihood to drive conversions.
-
U-shaped Attribution: Gives more credit to the first and last touchpoints (typically 40% each), and the remaining 20% is distributed evenly among the middle touchpoints.
-
W-shaped Attribution: Similar to U-shaped, but assigns significant credit (typically 30%) to the first touch, middle touch (often the lead conversion), and last touch, with the remaining credit evenly distributed among other interactions.
-
Full Path Attribution: Assigns credit to all key stages of the customer journey (e.g., first touch, lead conversion, and purchase), often with the credit distributed evenly or weighted based on the importance of each stage.
-
Custom Attribution: Tailored to a specific business's needs, this model allows marketers to define their own rules for assigning credit to touchpoints based on their unique customer journey and business goals.
Discrepancies in Attribution
Discrepancies occur when different systems report different attribution metrics for the same conversion events. These inconsistencies arise because various platforms use distinct attribution models, conversion windows, and tracking mechanisms. Common sources of discrepancies include:
-
Attribution Models: Platforms use different methods to assign credit (e.g., first-touch, last-touch, linear).
-
Conversion Windows: Platforms define different timeframes for attributing a conversion to an interaction, affecting which touchpoints are credited.
-
Click vs. View Attribution: Some platforms prioritize clicks, while others may also count views (exposure to ads without clicks).
These differences can lead to confusion in performance reporting and budget allocation decisions.
Webgains Default Attribution
-
Last-Network-Click Attribution: Webgains attributes conversions to the last click (within its own network) before a conversion, awarding 100% of the credit to that interaction. Clicks from other digital marketing channels, including other affiliate networks, are not considered in Webgains' attribution model. Any sale will be tracked if there was a click from the Webgains network within the designated cookie period.
-
Cookie-based and Server-to-Server Tracking: Conversions are tracked using cookies stored on the user’s device and server-to-server methods, improving reliability and accuracy.
-
Standard Conversion Windows: Defined on a program level by the client, typically ranging from 30 to 90 days.
Default Attribution in Other Systems
|
Platform |
Default Attribution Model |
Cookie/Tracking Mechanism |
Standard Conversion Window |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Last-click/View-through |
Cookie/Server-based |
7 days click, 1 day view |
|
Google Analytics |
Data-driven |
Cookie-based / Cookieless (Probabilistic) |
90 days |
|
Affiliate Networks |
Last-click |
Cookie-based / Cookieless (Probabilistic) |
30 days |
|
Adobe Analytics |
Customizable |
Cookie/Server-based |
30 days |
|
Twitter Ads |
Last-click |
Cookie-based |
30 days |
|
LinkedIn Ads |
Last-click |
Cookie-based |
30 days |
|
TikTok Ads |
Last-click/View-through |
Cookie/Server-based |
7 days click, 1 day view |
|
Pinterest Ads |
Last-click/View-through |
Cookie-based |
30 days click, 1 day view |
How Attribution Affects Reporting Discrepancies
Different platforms report conversions differently due to variations in attribution models, conversion windows, and tracking methods. These factors lead to discrepancies, which are important for marketers to understand when analyzing performance and making data-driven decisions.
-
Attribution Model Differences:
-
GA4 (Google Analytics 4) uses a data-driven attribution model, distributing credit across multiple touchpoints based on machine learning insights. This approach may assign credit to earlier interactions, even if the final conversion happens much later.
-
Affiliate Networks typically use a last-click attribution model, where only the last interaction (affiliate click) within a set conversion window gets credited.
Key Point: Each platform tracks only its own interactions and conversions. For example, GA4 might give credit to multiple touchpoints, while affiliate networks track only the last click within their window.
-
-
Conversion Window Variations: Conversion windows differ between platforms, impacting how conversions are attributed:
-
Facebook: 7 days click, 1 day view
-
GA4: 90 days
-
Affiliate Networks: 30 days
Key Point: A conversion reported by GA4 may not be counted by an affiliate network if it occurs outside their shorter window.
-
-
Tracking Mechanisms (Cookies vs. Server-based):
-
Some platforms (like Google Analytics and Facebook) use a combination of cookie-based and server-to-server tracking, while most affiliate networks rely on cookies alone.
-
Cookies are more prone to being blocked or cleared, leading to potential underreporting on cookie-dependent platforms if a user clears their cookies before converting.
Key Point: Platforms that use server-side tracking (like GA4) can track users more persistently than cookie-only platforms.
-
-
Impact on Data Reporting: Platforms with longer conversion windows or data-driven attribution (like GA4) will likely report more conversions than affiliate networks using shorter conversion windows and last-click attribution. Discrepancies arise because each platform only tracks conversions from its own interactions within its specific window.
What Does This Mean for Marketers?
Marketers should be aware that discrepancies in conversion reporting occur because of the differences in attribution models, conversion windows, and tracking mechanisms across platforms. Understanding these differences helps in making more informed decisions about:
-
Optimizing Reporting: Aligning conversion windows and attribution models across platforms helps create a more accurate comparison between data-driven models (like GA4) and last-click models (like affiliate networks).
-
Effective Budget Allocation: Discrepancies in reported conversions can mislead budget decisions. Marketers should ensure they understand how each platform tracks conversions to allocate resources more effectively.
-
Improving Campaign Strategy: Aligning conversion windows and attribution models will help marketers better understand how different channels interact in the customer journey, refining campaign strategies for improved performance.
Attribution FAQ
Q1: Difference Between Cookieless and Cookie-Based Tracking
-
Cookie-Based Tracking: Involves storing small text files (cookies) on the user’s device to track actions across sessions. It enables targeted advertising and analytics, but raises privacy concerns, especially with modern browser restrictions and regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
-
Cookieless Tracking: Uses alternative methods like server-side tracking, cookieless, or first-party data to track user behavior. It's seen as more privacy-friendly and bypasses cookie-blocking mechanisms, offering more persistent tracking, especially across devices.
Q2: Post-View vs. Post-Click Attribution
-
Post-Click Attribution: Attributes conversions to a user’s click on an ad, regardless of how long it takes for the conversion to happen. Useful for performance-based advertising where immediate action is expected.
-
Post-View Attribution: Gives credit to a conversion when a user views an ad, even without clicking it. This model helps measure the impact of ads on brand awareness or upper-funnel activities, where exposure may influence future decisions.
Q3: Why Do Different Platforms Report Different Conversion Numbers?
The discrepancy in conversion reporting comes from the unique attribution models, conversion windows, and tracking mechanisms used by different platforms. Platforms like GA4 use data-driven models that assign credit across multiple touchpoints and can track over longer windows, while others (like affiliate networks) focus on last-click attribution within a shorter window. These differences contribute to variations in the number of conversions reported by each platform.
Related Reading:
